Author: Dr. V. Rajasekhar
Senior Consultant Interventional Cardiology & Electrophysiology, Certified TAVR Operator & Clinical Director
Introduction
Premature Ventricular Complexes (PVCs) are common cardiac arrhythmias that often originate from the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT). While many PVCs are benign, frequent symptomatic PVCs—particularly from RVOT—can significantly impair quality of life and, in some cases, impact cardiac function.
Modern electrophysiology now offers an effective solution: Radiofrequency (RF) catheter ablation guided by advanced 3D mapping systems. This blog will take you through an actual case performed by Dr. V. Rajasekhar, detailing the clinical background, procedure, technology used, and outcome—along with FAQs for patient education.
Case Summary: Right Ventricular Outflow Tract PVC Ablation
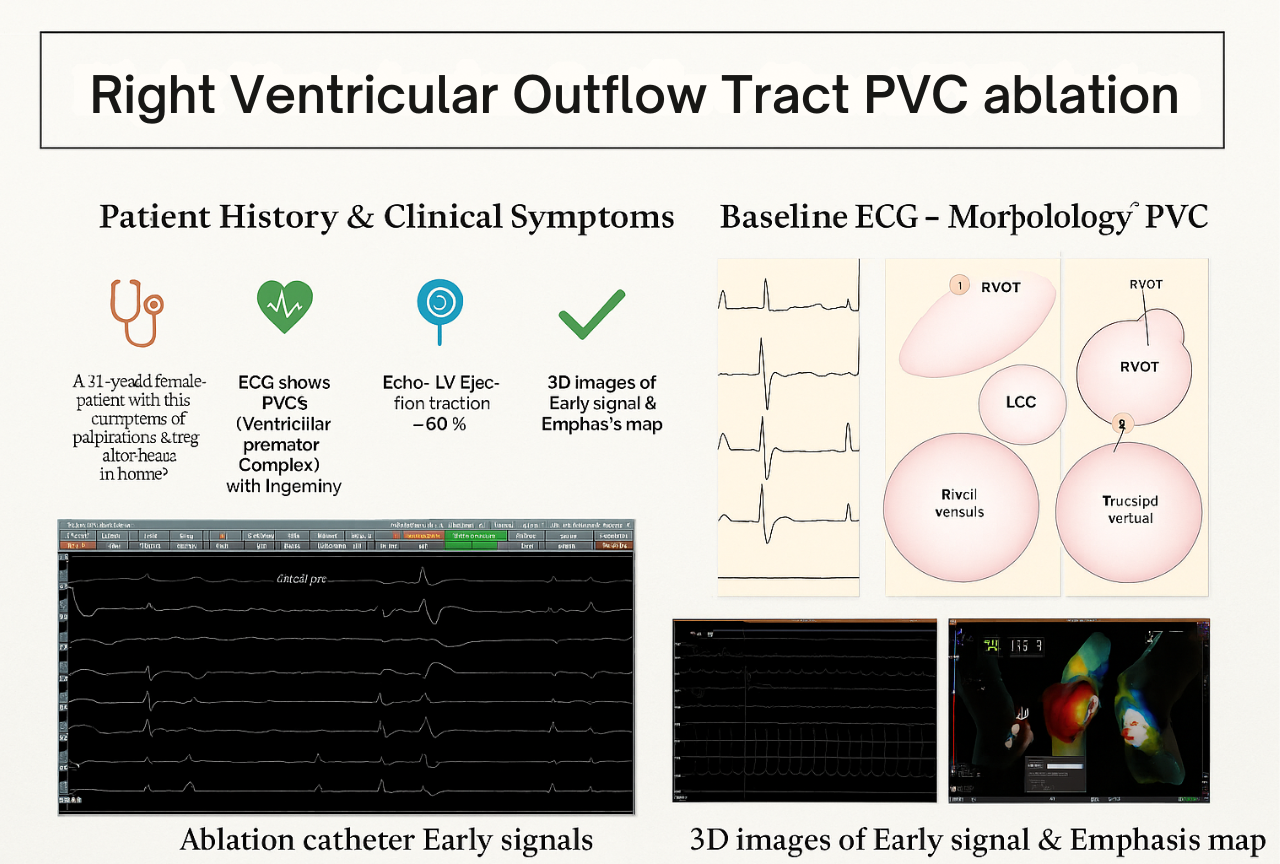
Patient: 51-year-old female
Symptoms: Palpitations and irregular heartbeats noted during home monitoring.
Clinical Workup & Diagnosis
📁 Patient History & Symptoms
- 51-year-old female presented with clinical symptoms of palpitations and irregular heartbeats.
- ECG revealed frequent Ventricular Premature Complexes (VPCs) with a trigeminy pattern.
- Echocardiogram showed a normal Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) of 60%.
- 24-hour Holter monitoring recorded PVC burden of 23%.
- Given the high symptomatic burden and frequency, the treatment plan included Electrophysiology Study (EPS) followed by 3D-guided RF ablation.
ECG Findings: Morphology of PVC
A detailed analysis of the baseline ECG helped in localizing the likely origin of the PVCs:
- Leads V1-V2: Negative R waves, indicating origin in the right ventricle.
- Leads II, III, aVF: Positive R waves, suggesting superior origin.
Anatomical suspicion: Right Ventricular Outflow Tract (RVOT).
Tools & Technology Used
Catheters and Mapping Systems
- Reference Lead: External ECG Lead III with maximal detection criteria.
- Roving Catheter: TactiFlex™ SE (Sensor Enabled) catheter with near-field detection.
Benefits of TactiFlex™ SE:
- Proprietary tip design
- Superior tip stability & signal quality
- Predictability of lesion creation
Advanced Mapping & Ablation
We utilized the Ensite™ X EP System, fully integrated with TactiFlex™, to map the early PVC signals and guide the ablation.
Key Advantages:
- Flexible tip for optimal contact
- Superior signal clarity
- Confidence in lesion placement
Electrophysiology Study & Ablation Procedure
Early Signals Detection
During EPS, early ventricular signals were identified 35 ms prior to the QRS complex using the TactiFlex™ catheter, confirming the target site for ablation.
3D Mapping & Targeting
3D electroanatomical maps were created, highlighting the early signal zones in RVOT with precision. This ensured that ablation was focused and efficient.
Suppression of PVC
During the ablation:
- PVC suppression was observed within 45 seconds, demonstrating immediate effectiveness.
- Both 2D and 3D views confirmed the elimination of PVC triggers.
Final Confirmation
Subsequent testing showed complete suppression of PVCs, confirmed with both 3D mapping and fluoroscopic imaging in RAO and LAO views.
Fluoroscopy Images
Radiographic confirmation was obtained through fluoroscopy:
Outcome
✅ The procedure was successful.
✅ Complete suppression of symptomatic PVCs.
✅ The patient was discharged with improvement in symptoms and better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are PVCs and why do they occur?
PVCs (Premature Ventricular Complexes) are early extra heartbeats that originate in the ventricles. They can occur sporadically in healthy individuals or be a sign of underlying heart conditions.
What is RVOT PVC ablation?
RVOT PVC ablation is a minimally invasive procedure where radiofrequency energy is used to eliminate abnormal heart tissue responsible for generating PVCs originating from the right ventricular outflow tract.
Who is a candidate for ablation?
Patients with:
- High PVC burden on Holter (>10-15%)
- Symptomatic palpitations
- PVC-induced cardiomyopathy
- Ineffective response to medications
How is the ablation procedure performed?
- The procedure is done under conscious sedation or anesthesia.
- Using advanced 3D electroanatomical mapping, the origin of PVCs is precisely identified.
- A catheter delivers radiofrequency energy to ablate the problematic tissue.
Is ablation safe?
Yes, in expert hands, PVC ablation is a safe and effective treatment with high success rates (>90% for RVOT PVCs) and low complication rates.
Will my symptoms resolve after ablation?
Most patients experience significant reduction or elimination of symptoms after successful ablation. It may take a few weeks to notice full benefits.
Are there any risks?
Minor risks include:
- Bleeding at catheter insertion site
- Rare arrhythmias
- Very low risk of cardiac perforation
Is hospital stay required?
Usually, it is a day-care or overnight procedure. Most patients can return home the next day.
What is the follow-up after ablation?
- ECG & Holter monitoring to confirm PVC suppression.
- Follow-up visits at 1, 3, and 6 months.
- Lifestyle counseling and medications if needed.
Is this a cure?
For idiopathic RVOT PVCs, the ablation success rate is high, and many patients experience long-term freedom from PVCs after the procedure.
Right Ventricular Outflow Tract (RVOT) PVC ablation represents a safe, effective, and durable solution for patients troubled by symptomatic PVCs. With the advent of sensor-enabled catheters like TactiFlex™ and 3D electroanatomical mapping, modern electrophysiology ensures superior outcomes with greater safety and predictability.
If you or your loved ones are suffering from persistent palpitations or irregular heartbeats, consult your cardiologist to evaluate if PVC ablation could benefit you.